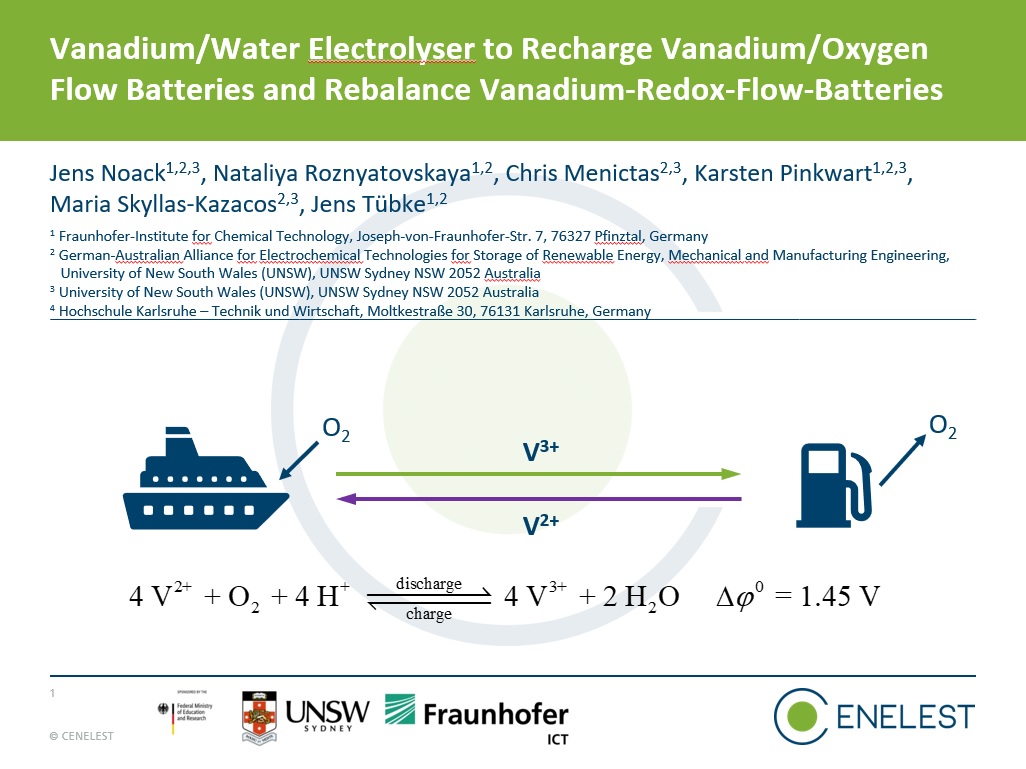
Jens Noack is giving a talk about Vanadium/Water electrolyser for recharging Vanadium/Air cells at the 29th Topical Meeting of the International Society of Electrochemistry in April 2021. topical29.ise-online.org/index.php
Talk at the 2021 International Renewable Energy Storage (IRES) Conference
Jens Noack will speak on March 17th at the International Renewable Energy Storage (IRES) conference about the latest research on Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries at Fraunhofer ICT and UNSW. https://www.eurosolar.de/en/index.php/events/ires-conference-eurosolar
Talk at the 239th ECS Meeting
Jens will talk on Tuesday June 1st at the 239th meeting of The Electrochemical Society about Vanadium/Air systems: https://ecs.confex.com/ecs/239/meetingapp.cgi/Paper/144954
The first publication in the field of iron/iron redox flow batteries
This open access publication is about investigations of different modes of operation and different materials with and without recombination cell to avoid charge carrier loss and thus to increase cycle stability. We have also investigated regeneration of the electrolyte with external hydrogen and successfully restored lost capacity. Iron/iron redox flow batteries thus form an interesting possibility with an exceptionally inexpensive and safe energy storage material.
Read the full article here: https://dx.doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abcf50
Publication in the prestigious Chemical Engineering Journal
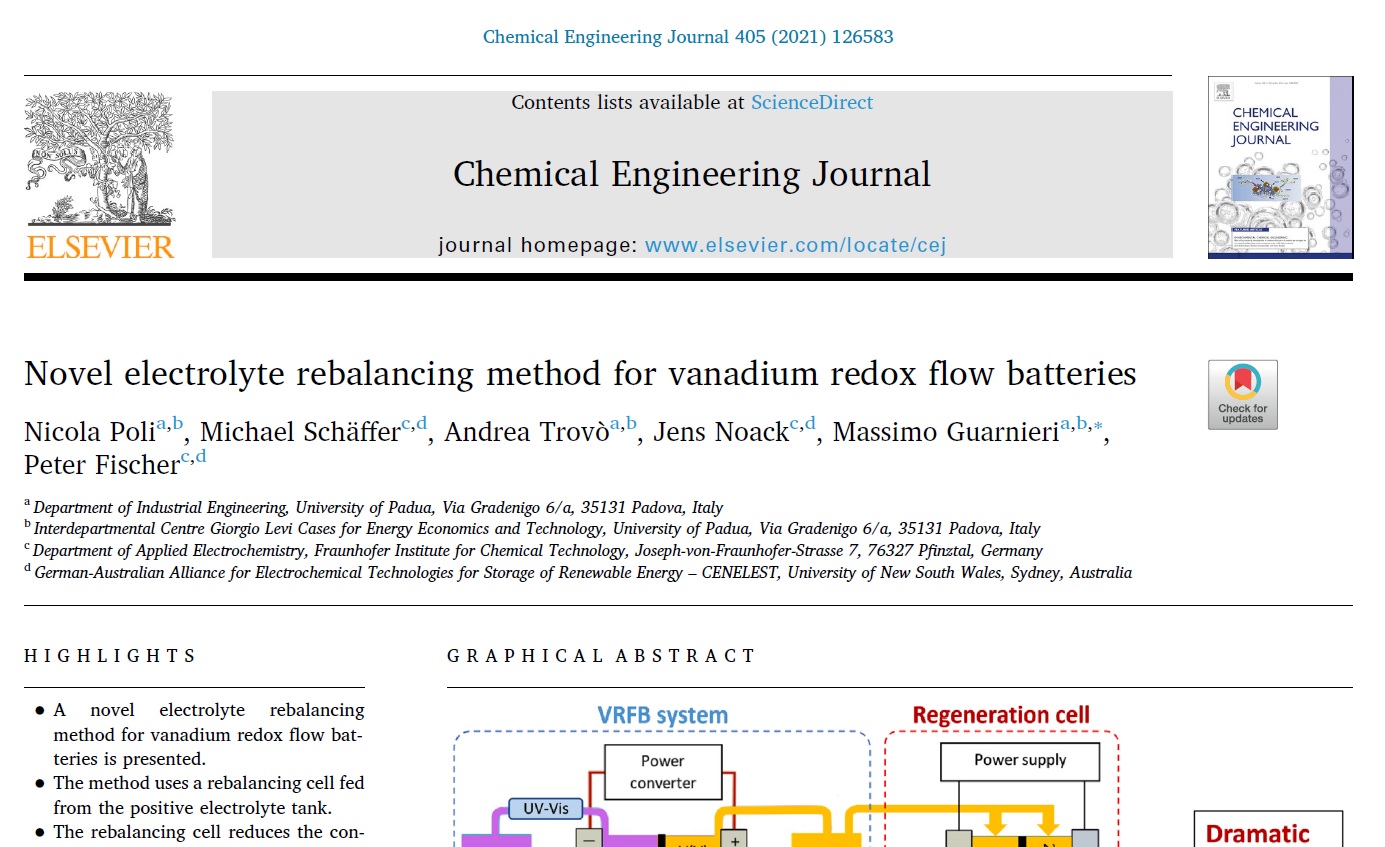
For almost three years now, a collaboration with the University of Padua in the field of redox flow batteries has existed with the Fraunhofer ICT. It is carried out through the Erasmus Mundus scholarship program between the group of Prof. Massimo Guarnieri at the University of Padua and the Department of Applied Electrochemistry. The results of the last master thesis in this collaboration of Mr. Nicola Poli have now been published in the prestigious Chemical Engineering Journal (Impact Factor 10.652).
Based on a patent of the Fraunhofer ICT the application of so-called regeneration cells was investigated. With the help of these cells, irreversible changes in the electrolyte, which lead to a loss of capacity, can be electrochemically compensated. One of these possible changes is the entry of oxygen, which can diffuse through the plastic parts of the battery. This entry can oxidize vanadium and thus lead to a permanent loss of capacity in the long run. With the help of a small extra cell, which produces oxygen and reduces the electrolyte again, this oxidation can be reversed and the state of charge of the electrolyte can be balanced again.
Such a cell can help to maintain the state of charge of a battery in the long term and make electrolyte maintenance unnecessary. The difficulty of the work was to achieve an end point determination of the charge balance without additional sensor technology. Nicola Poli could prove that this is possible by controlling the charge current. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S138589472032711X